|
Continuing Education Partnership:
The National Commission on Health Education Credentialing (NCHEC)
Contents:

About NCHEC - Why is this endorsement important?
NCHEC (pronounced N-CHEC), is the national body that certifies health educators. To see a brief video about NCHEC and its certifications, click here.
The designation of Certified Health Education Specialist (CHES) and Master Certified Health Education Specialist (MCHES) are marks of professional competency and commitment to continued professional development for persons in the field of health education. ICA, through its ToP courses, is a recognized provider of continuing education credits to these individuals.
- More than 10,000 health educators in the US need CHES credits to maintain their NCHEC certification.
- CHES and MCHES graduates of TFM and TSP and now TSI rave about the practical skills they have learned in ToP courses.
- Approved ToP courses get listed on NCHEC training calendar.
- ICA can label approved courses as offering CHES credits.
- ICA can communicate directly to CHES/MCHES professionals as often as monthly about approved courses.
- That means LOTS of new folks hearing about ToP.
Abbreviations decoded:
NCHEC - National Commission for Health Education Credentialing, Inc. The organization responsible for maintaining certification criteria and processes, managing continuing education programs and testing and certifying professionals.
CHES - Certified Health Education Specialist - "An individual who has graduated with a bachelor's, master's or doctoral degree from an accredited institution of of higher education with a degree in health education and or at least 25 semester hours of course work that addressed NCHEC's Seven Areas of Responsibility and Competency for Health Educators."
MCHES - Master 's level Certified Health Education Specialist - This is "an advanced-level practitioner that has: met required academic qualifications, worked in the field for a minimum of five years [and] successfully passed a competency-based examination" administered by NCHEC.
CECH - Continuing Education Contact Hour - this represents 60 minutes of instruction on content relevant to NCHEC's required competencies.
MEP - Multiple event provider - a status granted to organizations based on relevancy of courses offered, commitment to honor NCHEC requirements, and existence of process and structure to assure acceptable levels of quality in content delivery. ICA, through its collaboration with ToP Network, will be able to consider expanded course offerings in the future.
back to contents
Program Requirements:
For attendees of TFM, TSP or TSI courses wanting CHES credits, a trainer will need to:

- Have each CHES/MCHES course participant complete a course evaluation form specific for continuing health education contact hours (CECH). The evaluation is against course learning objectives and uses evaluation forms specific to those objectives established for that course.
- Provide a sign in sheet for CHES/MCHES participants that captures their CHES or MCHES number. This sign in sheet will include course name, location and dates, and number of CECH awarded.
- Provide a special CHES certificate to each person requesting CECH. That certificate must include: Participant name, CHES or MCHES number, course date and location and number of CECH earned.
- Upload a copy of the evaluation, a copy of the certificate and the roster with participant's name, CHES/MCHES number, course date and location and CECH earned to the NCHEC repository for ICA - this link is also accessed as the NCHEC Reporting Form page under the "Trainers" tab at www.top-training.net.
- The above documentation should be submitted within one week of the course completion. ICA-USA staff bundle these documents for submission to NCHEC. Direct questions to [email protected].
back to contents
CECH determination:
The number of CECH for each course is predetermined when a course is approved for CHES/MCHES credits. The hours are based on rules established by NCHEC. To be eligible for CECH, the person must:
- Be certified (or working toward certification) as CHES or MCHES by NCHEC.
- Attend the entire course for which CECH are being awarded (be present from start to finish).
- Submit a the NCHEC evaluation required evaluation form.

CHES Resources - Learning Objectives:
Each course approved for CHES credits will be evaluated against learning objectives that map to NCHEC competencies.
To review the current list of NCHEC competencies, click here. View the learning objectives that have been mapped to TFM, TSP, and TSI when taught in compliance with the ToP Trainers' Manuals.
Materials and Supplies:
Trainer CECH checklist: docx
Course sign in sheet template xlsx (Or customize your own sign in sheet to capture CHES/MCHES number.)
CECH credits reporting form -- submit to [email protected] within one week following the course. xlsx
Back to requirements
Qualification for CECH credits requires teaching the complete course as specified in the trainer and participant manuals. Approved variations are listed below.
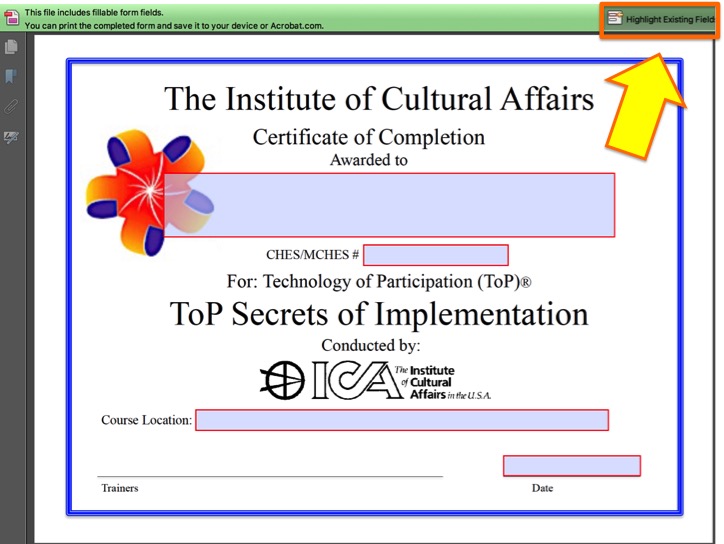 Course certificates may be completed by hand or computer - fields are pre-formatted and fillable. If form fields are not clearly visible after downloading, click box in the upper right hand corner to highlight them (See Image.) Certificates include 2 pages. Course certificates may be completed by hand or computer - fields are pre-formatted and fillable. If form fields are not clearly visible after downloading, click box in the upper right hand corner to highlight them (See Image.) Certificates include 2 pages.
back to contents
CHES/MCHES Learning Objectives:
ToP Facilitation Methods course:
Focused Conversation:
- Engage and facilitate cooperation among stakeholders.
- Help groups identify, reflect on, and verbally evaluate training needs and programs and the impact of these programs.
- Help groups or teams have meaningful conversations in order to develop evaluation and research questions.
- Facilitate group discussions to process relevant information and data.
Consensus Workshop:
- Plan and implement meeting strategies that engage participants in planning.
- Design meetings that build and promote collaboration, sharing of diverse concepts and ideas and construct consensus for planning action.
- Provide facilitation, guidance and consultation for meeting development and planning for health professionals and leaders in achievement of their learning and meeting objectives.
Action Planning:
- Use assessment, asset inventories and other data to guide and inform action planning. This addresses using data/information.
- Develop goals and specific actions with realistic outcome measures and identify champion or lead for the work. This addresses goal and strategy development.
- Identify and select a variety of action priorities and strategies/interventions to achieve the planning goals and outcome expectations. This addresses knowing and using various strategies.
- Practice an inclusive model for partner or stakeholder engagement.
Application and Design:
- Create meeting designs to achieve the desired objectives of the group using proven group processes and best-practice methods. This addresses meeting and learning session design.
- Promote engagement and participation through meeting design and facilitation strategies, using reflection and evaluation to gauge meeting effectiveness. This addresses individual skill building, evaluation of goal achievement, and reflection of meeting achievements.
- Plan with meeting partners and stakeholders to design, implement, and evaluate the session outcomes. This addresses collaboration, partner participation, and feedback and evaluation of both the meeting and the expert assistance.
ToP Strategic Planning:
Practical Vision Workshop:
- How to enable a group to clarify their 3-5 year vision in such a way that it motivates them to implement the plan.
- Develop goal statements.
- Formulate measurable objectives.
- Development training objectives.
- Create purpose statement.
- Promote collaboration among stakeholders.
Underlying Contradictions Workshop:
- Understand how to help a group discern the key factors that are blocking the realization of their vision.
- Engage stakeholders to participate in an assessment process
- Examine factors that influence the learning process;
Strategic Directions Workshop:
- How to help a group determine the most effective strategies to implement their vision.
- Design strategies
- Use communication strategies
- Facilitate cooperation among stakeholders
- Develop strategies to enhance career development.
Focused Implementation Workshop:
- How to help a group build a plan to ensure the implementation of their long range vision in a way that sustains momentum.
- Develop a sequence for the delivery of health education
- Use evaluation findings to plan future training
- Implement strategies to enhance career development
- Implement training sessions and programs.
back to objectives
ToP Secrets of Implementation
PHASE 1: Getting Started
- Understand the keys to effectively launch and implement a strategic plan.
- Enhance individual confidence to implement a plan.
- Engage and guide stakeholders to plan and implement.
- Describe four phases of the implementation journey.
- Engage group in assessing factors that impact motivation and ability to implement and execute strategy.
- Use peer-mentoring processes to analyze and evaluate existing situations efforts
PHASE 2: Building and Sustaining Momentum
- Use a peer-mentoring model to encourage transparent communication to support program assessment and team efforts.
- Understand the keys to building and sustaining momentum.
- Apply a tool to identify relevant stakeholders and their strategic roles.
- Recognize organizational factors (e.g., training, coaching, mentoring, leadership, common vision) that will support team success in moving the plan forward.
- Practice a tool for exploring solutions.
PHASE 3: Re-Maneuvering and Making Adjustments
- Understand the keys to adapting the plan to effectively respond to emergent challenges.
- Reframe failures as learning opportunities for overcoming obstacles.
- Apply processes for planned and spontaneous review to keep plan on track.
- Practice models for both anticipated and unanticipated reviews to create necessary plan adaptations.
PHASE 4: Bringing Closure
- Understand the keys to effectively ending a project positively.
- Design closing events that review implementation effectiveness and celebrate contributions and learning.
- Facilitate telling the story of the implementation journey.
- Understand the facilitator competencies necessary to support the implementation journey.
back to contents
|





 Course certificates may be completed by hand or computer - fields are pre-formatted and fillable. If form fields are not clearly visible after downloading, click box in the upper right hand corner to highlight them (See Image.)
Course certificates may be completed by hand or computer - fields are pre-formatted and fillable. If form fields are not clearly visible after downloading, click box in the upper right hand corner to highlight them (See Image.)